Final Results
Children's Learning Outcomes
By 2007, Tanzania achieved 97 percent enrollment among primary-school aged children. However, although primary school enrollment is high, students’ performance—albeit improving—remains poor. Over the last decade, pass rates for the Primary School Leaving Exam (PSLE), an exam taken at the end of Standard 7, have ranged from a low of 30 percent in 2012 to nearly 60 percent in 2011 (MoEVT 2015). In 2016, 67.8 percent of Tanzanian students passed the PSLE, suggesting that education reforms, teacher training, and other interventions may be effective. Still, students’ early grade reading and math outcomes at Standard 3—although improving—remain poor and below government targets, indicating that students are not acquiring foundational academic skills.
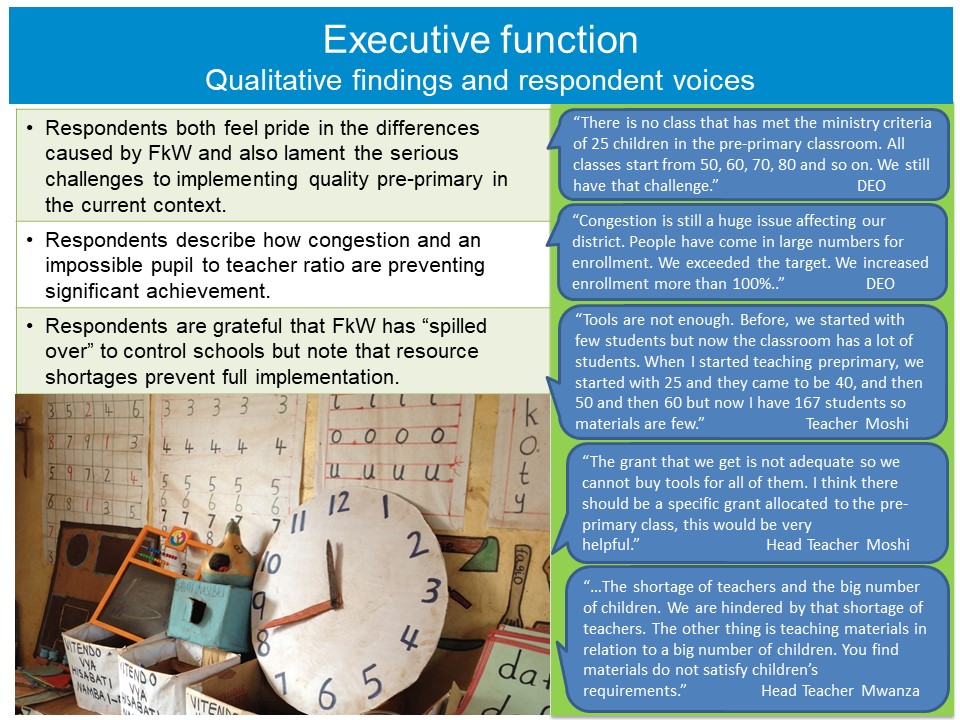
Given students’ underperformance in learning outcomes across the primary grades, Tanzania is striving to improve teacher quality and effectiveness, the learning environment, and other factors critical to student performance. Policymakers and implementers have increasingly focused on early childhood education (ECE) given the growing global awareness of the critical role that quality pre-primary education plays in laying the foundation for improved school readiness and learning outcomes.
We wanted to assess how FkW impacts student outcomes. The FkW Learning Collaborative determined we should conduct a student assessment to gather preliminary evidence on student learning and development and explore whether FkW leads to improved outcomes among pre-primary students. We investigated different tools – including the concepts they measure, whether the tool had been validated in Tanzania, and how the tool was administered – and decided to use the student assessment tool developed by the Measuring Early Learning Quality and Outcomes (MELQO) initiative.
What is MELQO?
MELQO is a global effort to promote improved measurement in early childhood. Lead agencies: UNESCO, UNICEF, World Bank and The Center for Universal Education at the Brookings Institution. Click to learn more. The Measuring Early Learning Quality and Outcomes (MELQO) initiative aims to improve early childhood education worldwide through measurement of children’s development and learning and the quality of learning environments. Led by UNESCO, UNICEF, the World Bank, and the Center for Universal Education at the Brookings Institution, MELQO comprises an international consortium of individuals and institutions working to improve outcomes for young children by making early learning assessment more accessible around the world. MELQO’s measurement modules propose a core set of items with relevance across countries, with the goal of devising items that are globally comparable but locally adaptable.
Measuring student outcomes in the Learning Agenda
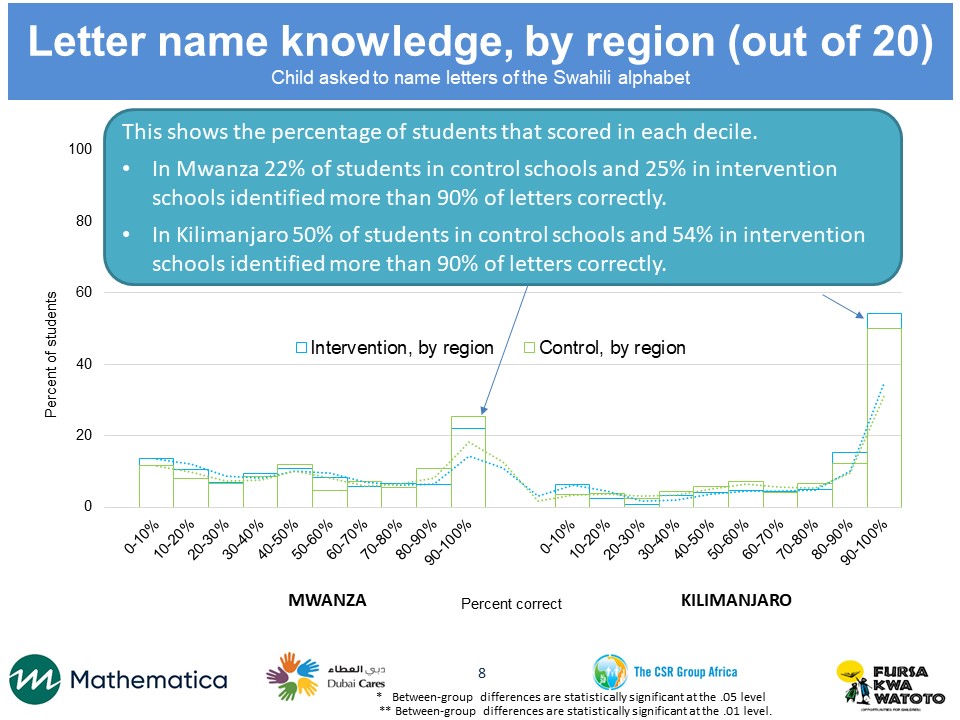
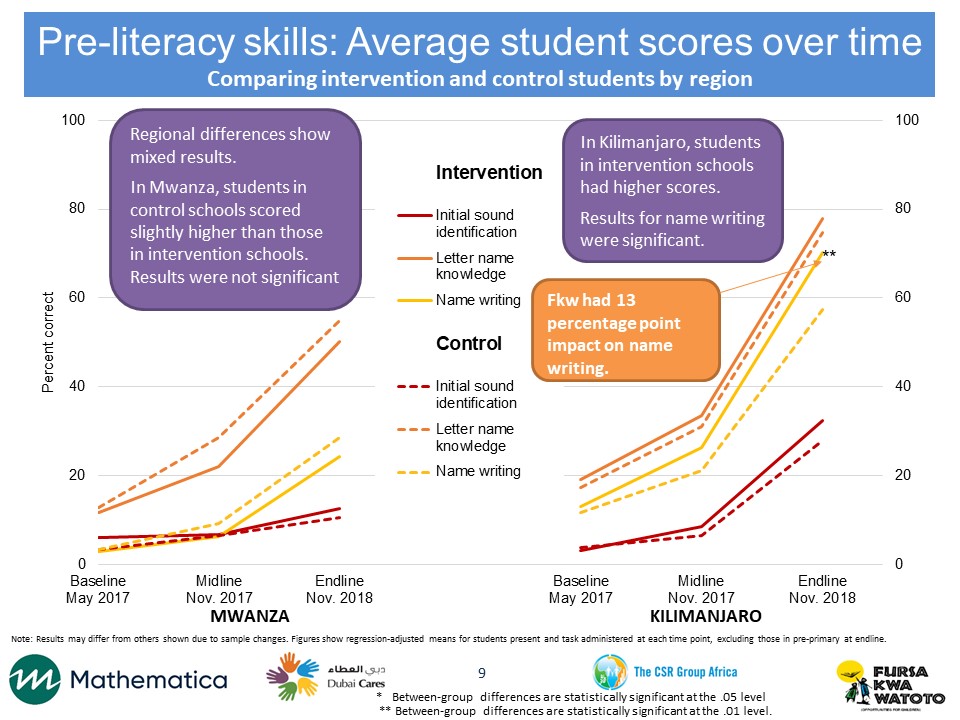
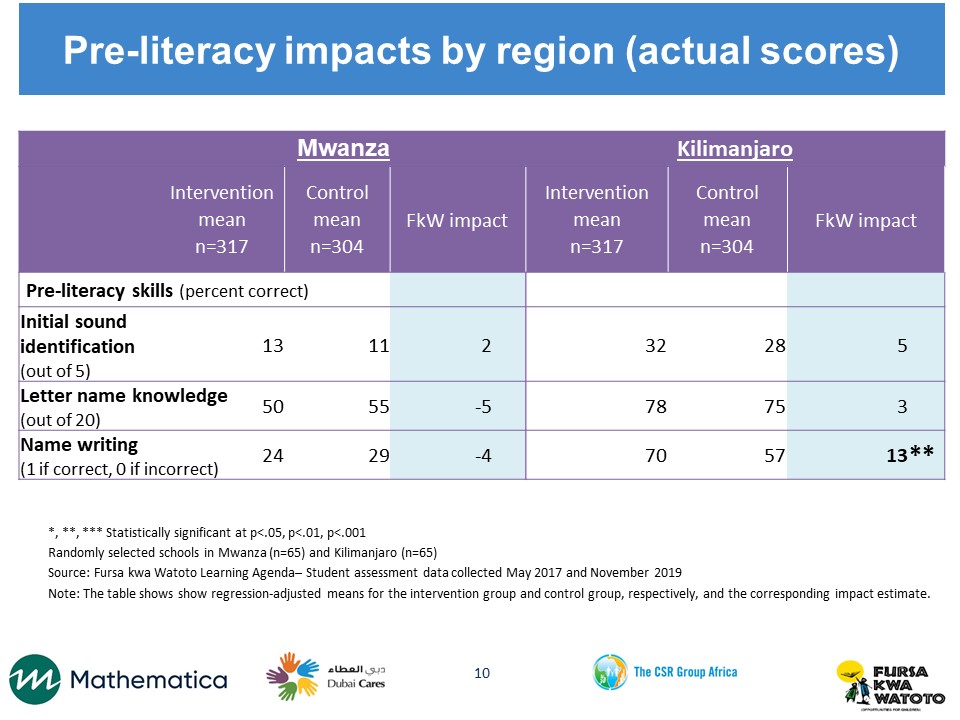
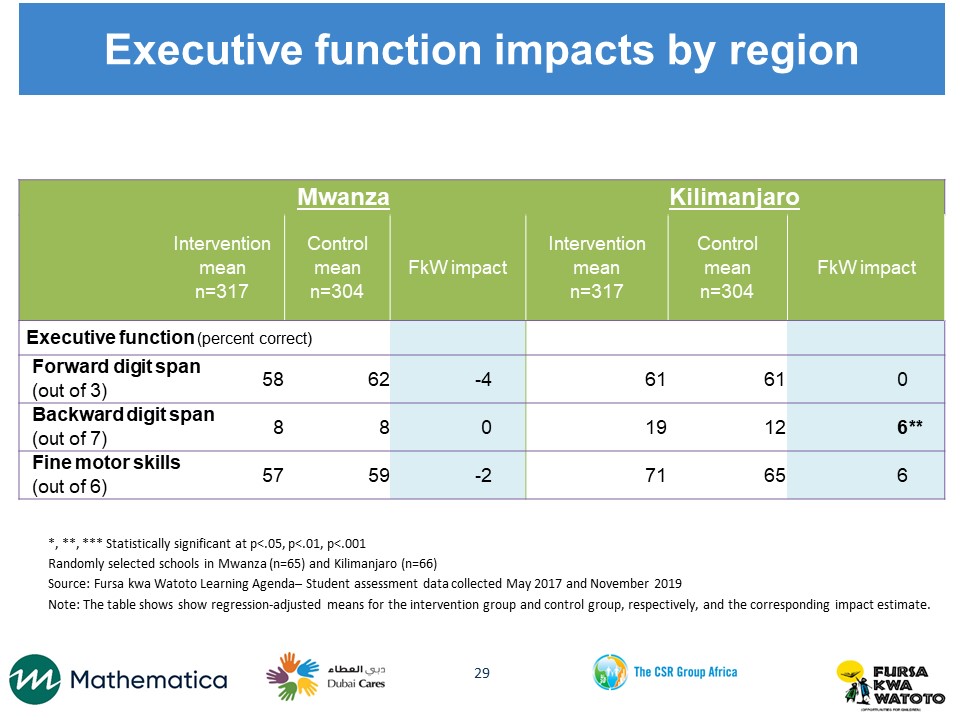
We conducted the MELQO assessment at two points, in May and November 2017. Our sample includes 131 randomly selected schools in Kilimanjaro and Mwanza regions. Schools were randomly assigned to the FkW intervention or the control group so that the study groups were similar on school-level characteristics before the intervention was implemented. Our field team worked with teachers to group students by age. In each of these schools, we listed the children’s ages and randomly selected 12 students—ages five or six—to participate in the assessment. We plan to follow the students for one additional year and conduct a follow-up assessment that combines MELQO and items from the Early Grade Reading and Mathematics Assessments, which are appropriate for older children, in order to assess whether the effects of FkW persist one year later.
Links to policy briefs and presentations
Presentation at Regional Dissemination Meetings
Meeting Brief: Outcomes and impacts of FkW on student learning and development
Outcomes and impacts of FkW on student learning and development
Social emotional development and executive functionClick here for more information and to see results from the Learning Agenda MELQO study.